Climate change Impacts Financial Stability
Human activity continues to drive climate change at an alarming rate and fuels disruptive weather events. It represents systemic risk that could result in disruptive changes across economic sectors and regions in the near term. It also represents opportunities for companies through participation in the transition to green economy. Now more than ever it is critical for companies to consider the impact of climate change and associated mitigation and adaptation efforts. To do that, they need clear, comprehensive, high-quality information on the impacts of climate change.
$29 T
Global Assets
Over $30 Trillion of assets under management are linked to ESG funds today.
1.5º C
Temperature Rise
Expected average rise in global temperature by 2050.
1.2 B
World Population
Expected population to be displaced du to climate change related causes by 2050.
“Every company, investor & bank that screens new & existing investments for climate risk is simply being pragmatic”
Jim Yong Kim, President of the World Bank
ESG Reporting Evolution
In less than 20 years, the ESG movement has grown from a corporate social responsibility initiative launched by the United Nations into a global phenomenon representing more than US$30 trillion in assets under management. Investors and other stakeholders are increasingly demanding companies disclose their ESG risks, practices, and impacts.
Increased popularity is also ushering in standardization in ESG reporting. Many new frameworks like GRI, CDP, SASB, TCDF, and WDI provide ESG reporting guidelines for businesses. Several legislative proposals requiring companies to disclose ESG-related information are currently being prepared or have become effective. With climate change posing risks and opportunities, businesses are increasingly focusing on disclosing its financial impact on their bottom line in their ESG reports. The metrics that help assess the impact of climate change are becoming ever so important.
TCFD
Task Force on
Climate Related
Financial Disclosures
TCFD provides information to investors about what companies are doing to mitigate the risks of climate change, as well as be transparent about the way in which they are governed. Established in 2015 by the G20 Financial Stability Board, its is adopted by over 1500 organizations worldwide and will become mandatory for ESG disclosures in many countries.
Earth Observation Indices™
Metrics For Climate Risks
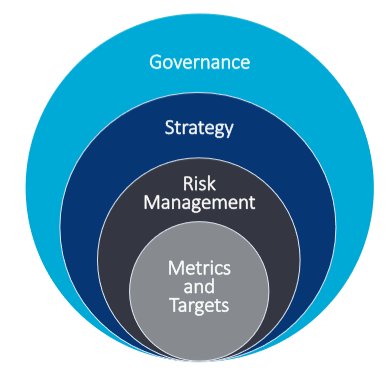
Core to the TCFD disclosures are metrics. The metrics quantify climate trends and projections and help assess a company’s exposure to the climate hazards and opportunities. Climate trends however often represent abstract concepts like drought and fire risks, and are notoriously difficult to quantify at local level and through time.
That’s where we come in. Our Earth Observation Indices™ track climate metrics including soil moisture, precipitation, wind speed, greenhouse gas emissions, etc. Our indices are derived from authoritative data sources, measure past trends as well as future projections and fit right in as inputs for the risk models of our clients.

